Rings in Ophthalmology is very important for diagnosis of disease by using specific ring names. It is also frequently asked questions in any ophthalmology exams. Rings in ophthalmology that means rings in eyes were mainly seen on three parts of an eyeball that are cornea, lens and posteroir segments.
Table of Contents
Rings in Cornea
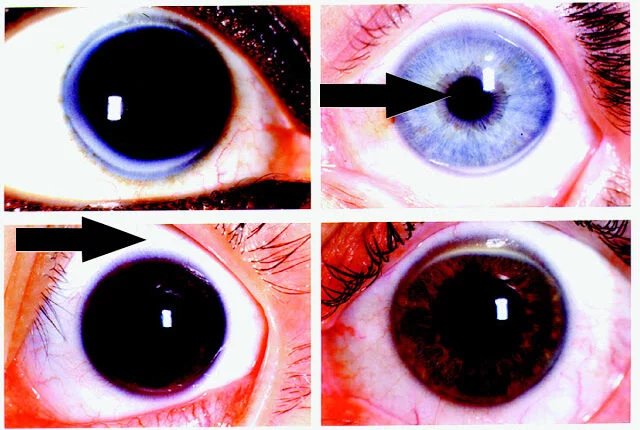
Arcus Senilis
These are commonly seen rings in eyes. Corneal grey ring-shaped degeneration is seen in old age patients. It have no symptoms, it doesn’t cause blurring of vision so it doesn’t need any treatments. Arcus senilis is made of fatty substances called lipids (mostly cholesterol). It usually starts from the middle age or later, if someone have this type of ring in childhood or before middle age it is termed as arcus juvenilis, it may be due to high cholesterol or other health problems.

Ring Abscess or Ring Keratitis

It is the hallmark of acanthamoeba Keratitis. It is vision threatening parasitic infeciton of cornea, this type of infections mostly seen on contact lenses wearer who doesn’t maintain proper lens hygiene. Stromal ring shaped infiltration were seen in this type of keratitis.
Kayser-Fleischer’s Ring
It is a copper deposition in Descemet’s membrane secondary to Wilson’s disease. Wilson’s disease is a genetic disorder causing excessive copper accumulation in body mostly in liver, brain and other organs. These rings starts from superior cornea, then it exapanded to inferior and finally circumferential peripheral corneal rings were seen.
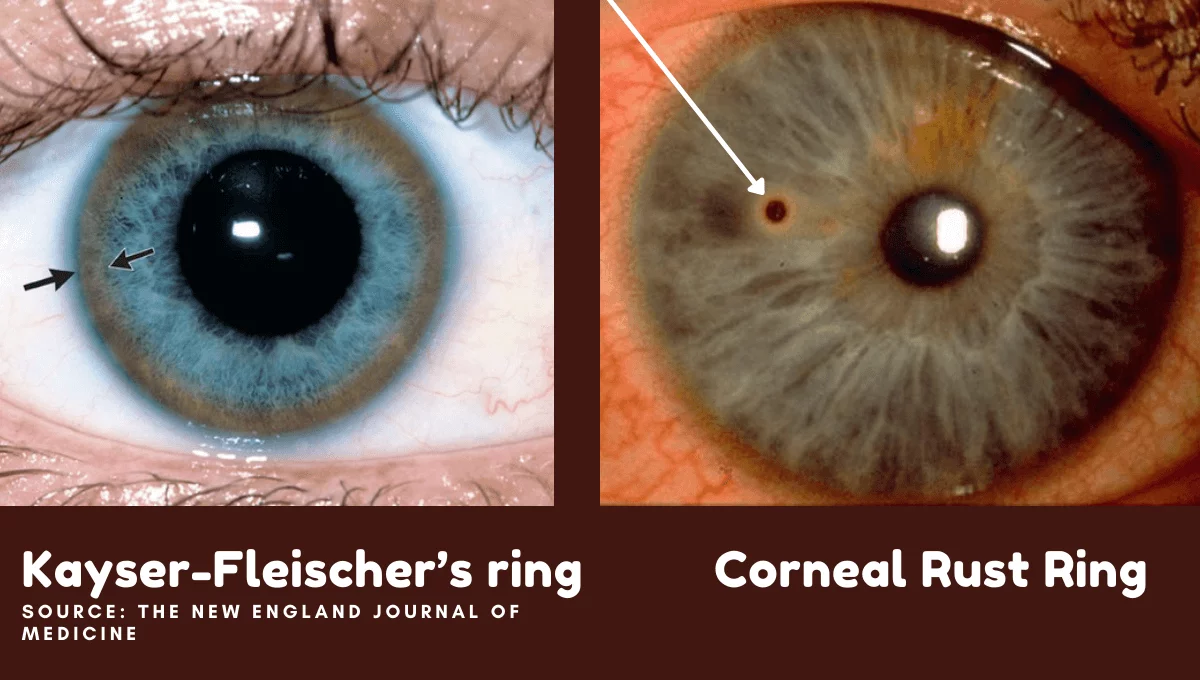
Corneal Rust Ring
A small, reddish-brown, circular Opacity in the Cornea after the metalic foreign body sticks in cornea. Sometime after removal of metalic foreign bogy the rust ring will be remain there. Ophthalmologist will remove by using hypodermic sterile needle or foreign body removal spud.
Coats’ White Ring
Fine iron deposits in the bowman’s layer remaining after a corneal foreign body. Sometimes this conditions were asymptomatic. These rings shapes were be round, oval or pear shaped. Coats’ White Ring mostly occurs after focal corneal injury.
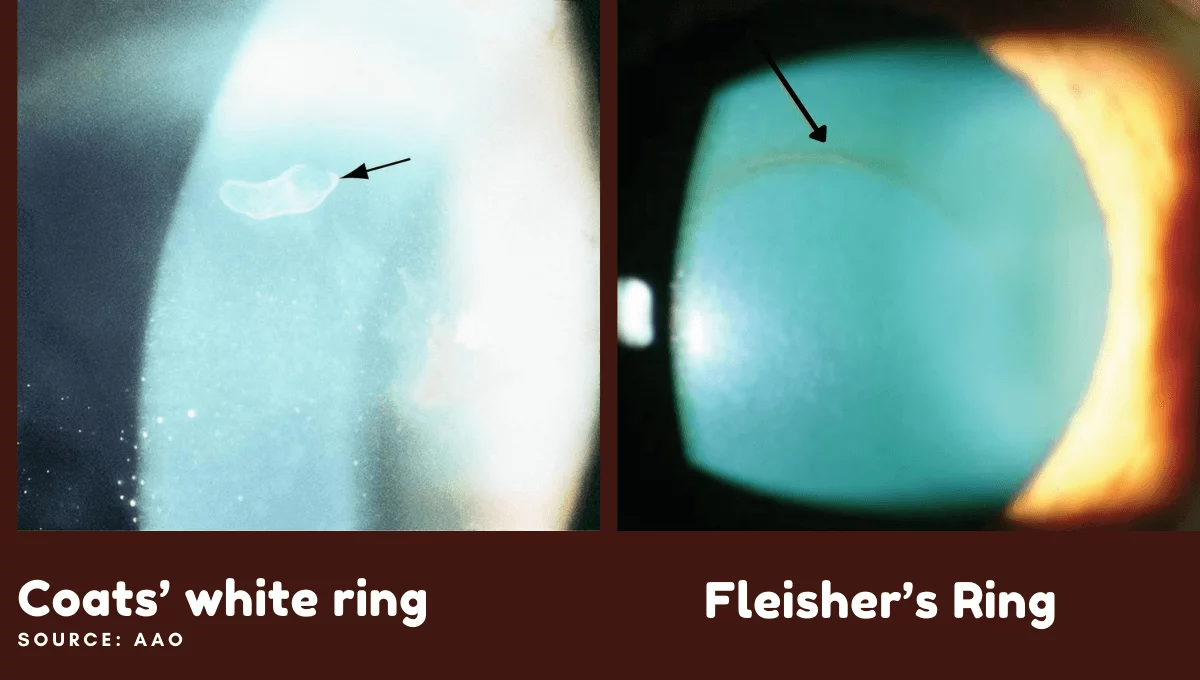
Fleischer ring
Visible iron deposition all around the base of a cone in keratoconus. Fleischer ring of iron deposition seen in keratoconus patients. These rings will best visible under cobalt blue light. It is indication of patient having Keratoconus eye disease.
Difference between Kayser-Fleischer’s Ring and Fleischer ring is that the Kayser-Fleischer’s Ring is copper deposit seen in Wilson’s disease while Fleischer ring is an iron deposit seen in Keratoconus.
Pseudo-Fleischer ring
Corneal iron deposition is seen in hyperopia.
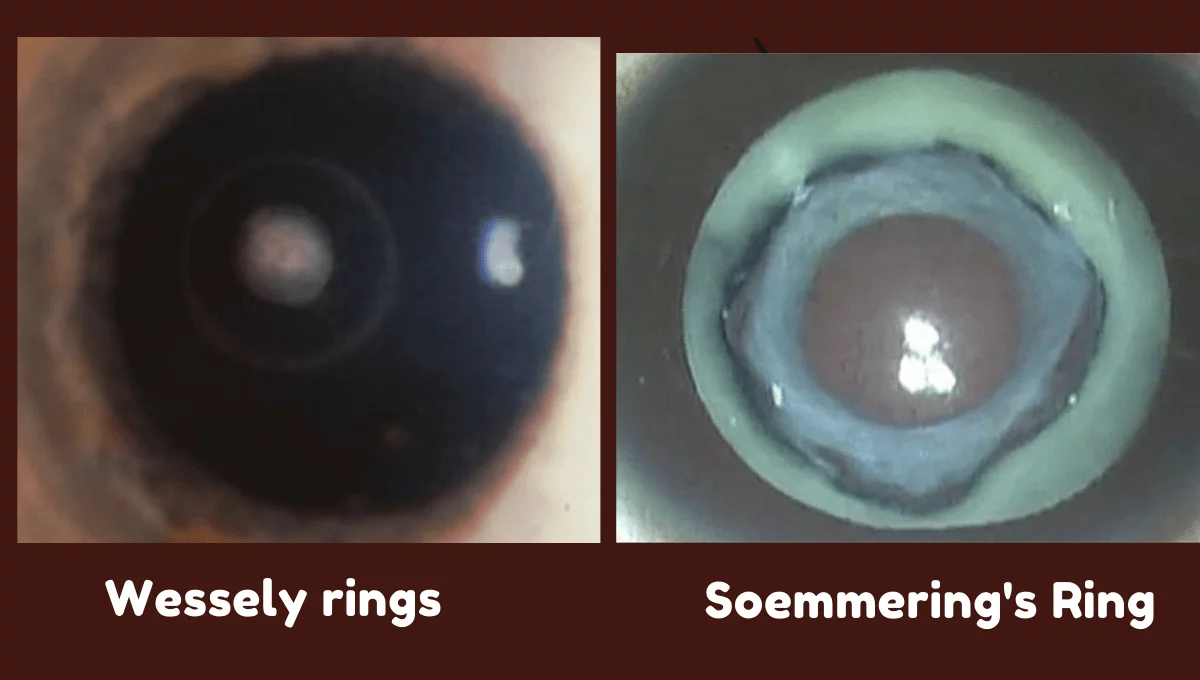
Wessley Immune Ring
Wessely rings are sterile, corneal intrastromal reactions resulting from immune response to foreign antigens. It can be found in various corneal infections as well as in non-infectious processes. These type of ring formation can be associated with microorganism which causes infections on cornea, or they can be sterile corneal infiltrates.
Ophthalmology Rings in Lens
Soemmering’s Ring
Early opacification of the posterior lens capsule in traumatic cataract. It is usually doughnut shaped ring present at lens capsule. Cases like pseudophakia, aphakia or in trauma in eyes these type of ring were visible.
Vossius’ ring
This is a very important ring in ophthalmology to rule out ocular trauma. Pigment deposition on the lens in concussion injury to the eye. Vossius ring is a well-circumscribed complete or incomplete ring of pigment deposited on the anterior lens capsule surface, usually as a result of significant blunt eye trauma.
This ring was first described by Vossius in 1903 AD, at which time he discussed both a pigmented variety of ring and a non- pigmented variety that he thought was a result of degeneration of anterior lens epithelial cells. The non-pigmented form is no longer considered to be a Vossius ring. When the eye is injured, a circular ring of fainted or stippled opacity is seen on the anterior surface of the lens due to brown amorphous granules of pigment lying on the capsule. It has the same diameter as the contracted pupil, and is due to impression of the iris on the lens as a result of the force of a concussion injury, which drives the cornea and iris backward.
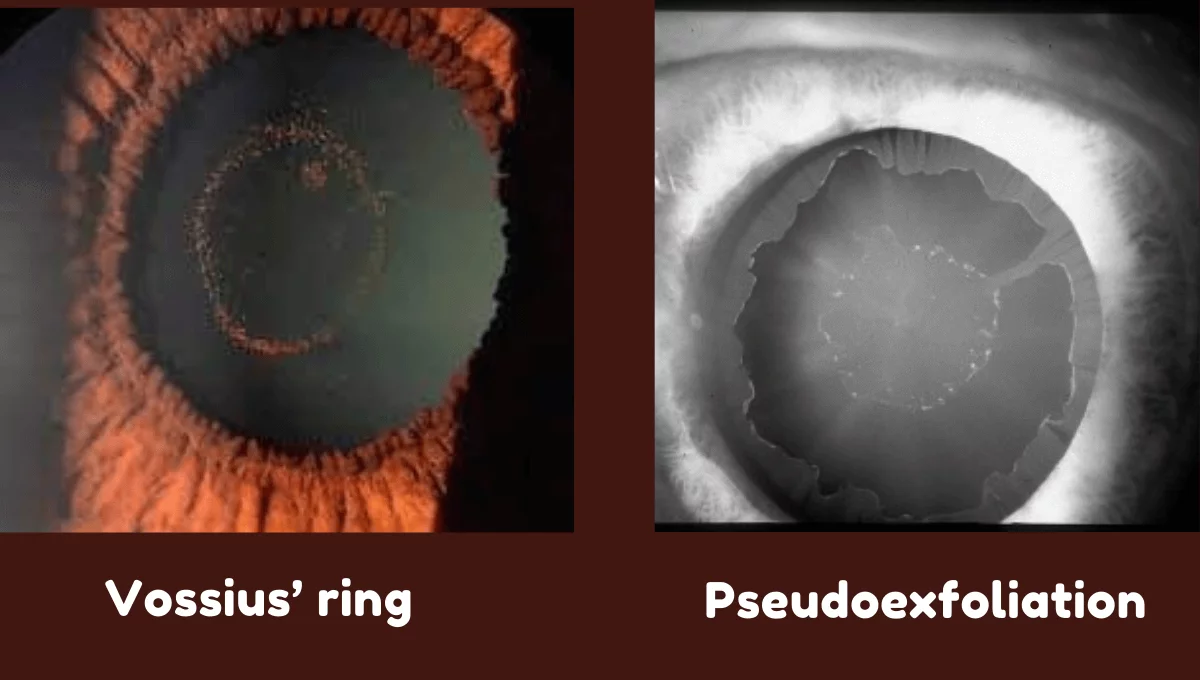
Hoarfrost ring
Pseudoexfoliation deposits on the anterior lens capsule. Pseudoexfoliation syndrome is a systemic disease with primarily ocular manifestations characterized by deposition of whitish-gray protein on the lens, iris, ciliary epithelium, corneal endothelium and trabecular meshwork.
Zentmayer ring (Scheie stripe)
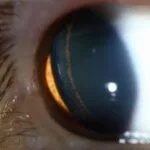
Pigment deposition in Pigment dispersion syndrome can occur at the insertion of lens zonular fibers into the posterior lens capsule and cause a pattern known as a Zentmayer ring or Scheie stripe. A circle of pigment seen on the posterior lens capsule at the insertion of the lens zonules.
Capsular Tension Ring (CTR)
Surgical device indicated for the stabilization of weakened, broken, or missing zonules that are suspected or observed during lens extraction. CTR are designed to maintain the capsule’s contour (equator ring) and to stretch the posterior capsule (tension ring), Capsular Tension Rings were originally used for zonular reinforcement in eyes with a weak zonular apparatus, such as in pseudoexfoliation and Marfan’s syndrome, and when zonular rupture or dehiscence occurs after blunt or surgical trauma.
Posterior Segment Rings in Ophthalmology
Weiss ring
Seen in hypoplasia of the optic disc This ring is a type of vitreous floaters. These are pieces of debris that float around in the vitreous humor of the eye, which is the gel-like substance lies between the lens and the retina. Floaters are often caused by shrinkage of the vitreous humor, causing tiny specks of collagen-like material to become visible as floating spots or threads in your field of vision. It is more common on old age population. A Weiss ring is a much larger, ring-shaped floater that is created by a posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) from around the optic nerve head. In other words, this is when the vitreous tissue detaches from the retina. One (most common) or multiple large floaters that are circular, ovoid or shaped in a bent line. This is also one of the common ophthalmology rings.
Double Ring Sign
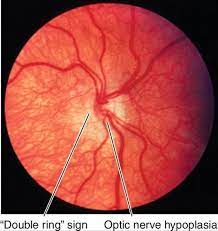
In optic nerve hypoplasia, optic disc is often pale or gray and smaller than normal. Optic discs often present with double ring sign yellow to white ring around the disc. A ring of hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation often, but not always surrounds the disc defining the area of the putative scleral canal. The outer ring represents the normal junction between sclera and the lamina cribrosa; the inner ring represents the abnormal extension of retina and pigment epithelium over the outer portion of the lamina cribrosa. Tortuous retinal arterioles, venules, or both may accompany optic nerve head, but retinal vessels can also present with normal caliber.
Ring scotoma
Annular visual field defect centred on the fixation point Age-related macular degeneration in the elderly and hydroxychloroquine toxicity in younger patients are usual causes of central ring scotoma
Summary of Rings in Eyes